In today’s landscape of digital interactions, chatbots have proven to be transformative agents, changing the way businesses engage with their audience. AI bots are a fusion of artificial intelligence and natural language processing; chatbots are virtual conversational agents that can understand, interpret, and respond to user queries in real time.
From streamlining customer support and automating routine tasks to delivering personalized interactions, chatbots enhance user experience across industries. In this era of instant connectivity, chatbots offer efficiency, accessibility, and a seamless bridge between users and businesses.
By 2027, Chatbots can become the primary customer support channel for a quarter of all the companies – Gartner
What is a Chatbot?
Omnichannel Chatbot is a software application or a conversational interface that simulates human-like conversations with users, often providing customer support. Chatbot can work with text or voice input and can be integrated into multiple customer channels like websites, Mobile Apps, Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Instagram, Telegram, Slack, and more. A chatbot helps businesses in automating customer support and engagement through workflows and artificial intelligence.
An AI chatbot is capable of responding in text or voice, replicating human-like conversations; chatbots can be as simple as a computer program that responds to simple user queries or as flexible enough to respond to all kinds of complex user queries, extending its scope.
Types of Chatbots
Rule-based Chatbots
Rule-based chatbots follow predefined flows/rules. These work on static decision trees based on keywords or option selection. They respond based on specific keywords or option-selection. These bots are easy to build but limited in flexibility and unable to understand natural language.
AI-powered (Intent-based) Chatbots
These chatbots use Natural Language Understanding (NLU) to identify user intents and extract entities. They can handle a wider range of user queries and respond with more contextual relevant responses. They often rely on platforms like Dialogflow, Rasa, or Floatbot's NLU engine.
Generative AI (LLM-based) Chatbots
These chatbots are powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT, these chatbots go beyond intents and entities matching — they can generate human-like responses in real time. They don't rely on predefined responses and can adapt to a variety of queries, even those not previously trained.
Hybrid Chatbots (Rule + AI)
These bots combine rule-based flows with the flexibility of AI. When the AI is not able to respond confidently, the bot takes rule based approach or can also be configured for live agent chat.
Voice-enabled Chatbots
Apart from how it is configured, these bots support voice inputs and can respond back with voice output as well. These bots have mic enabled which let users to send voice input and it processes using ASR and TTS. In return either it can return voice file and / or along with text output as well.
Agentic AI Chatbots (Goal-based Agents)
Built using Agentic workflows, these bots are driven by goals rather than just intents. They break down tasks into smaller sub-tasks and reason through them using AI planning capabilities.
How does the chatbot work?
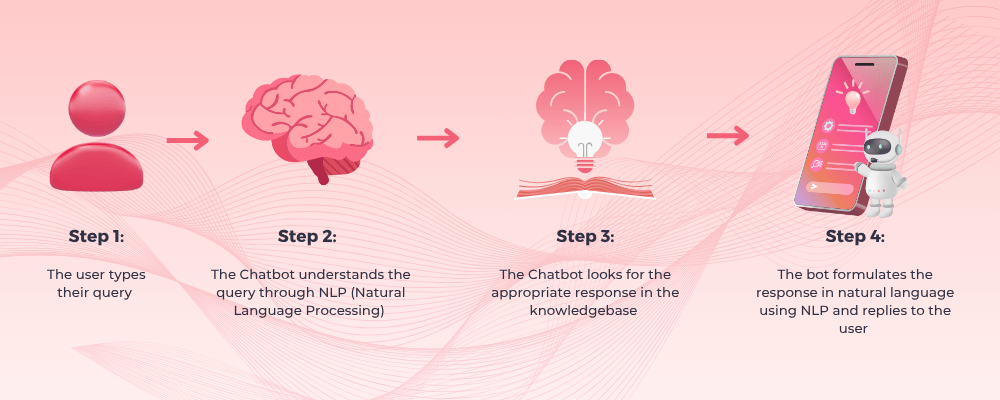
Workflow-based chatbots work on predefined flows intended to perform specific tasks and might not involve any underlying AI to process the data. Whereas conversational chatbots work as below.
-
User input: Users interact with the chatbot by typing or speaking the queries or commands into the chat interface.
-
Natural Language Processing: NLP enables bots to interpret and understand user input. It involves breaking down user messages into structured data that the bot can analyze.
-
Intent recognition: Chatbots identify the user's intent by analyzing the input. They determine what the user is trying to achieve or the information they are seeking.
-
Entity recognition: Entities are specific pieces of information within the user's input, such as dates, locations, product names, etc. Chatbots use entity recognition to extract these details and understand the context of the conversation.
-
Response: The chatbot generates a response in a natural language format that is understandable to the user. This response is then presented in the chat interface.
There are a number of natural language processing-based algorithms used to train chatbots; here are a few popular ones
- Naïve Bayes Algorithm
- Support vector Machine
- Natural language processing (NLP)
- Recurrent neural networks (RNN)
- Long short-term memory (LSTM)
- Markov models for text generation
- Grammar and Parsing Algorithms
Algorithms help chatbots learn from the data it is trained on, and to create an effective chatbot, you should use a good well, trained AI model.
Benefits of a chatbot
Improved Customer Service
Before the advent of chatbots, customer service required human intervention, which limited a business's availability for 24/7 support. In contrast, chatbots enable businesses to provide round-the-clock assistance, ensuring customers receive help whenever they need it. Bots can efficiently handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues.
Cost Reduction
Hiring contact center agents to provide 24/7 support can be both challenging and expensive. Not only is hiring costly, but ensuring consistency in responses requires training, which adds to business expenses. Training agents consumes significant time, and 70 to 80% of customer queries are repetitive and do not require human intervention. By deploying a chatbot, businesses can offer support 24/7, reducing the need for human agents. Chatbots can handle initial support and eliminate repetitive queries, allowing human agents to focus on more critical tasks. This helps businesses scale efficiently and meet the increasing demands of customers.
Enhanced Customer Engagement
Chatbots provide personalized and timely responses, interacting with customers and suggesting products or services based on past interactions. Additionally, chatbots are omnichannel, allowing users to chat on their preferred platforms. They also support multiple languages, enabling users to interact in their preferred language and remember user preferences for future interactions.
Increased Efficiency and Lead Generation
Chatbots can manage multiple customer interactions simultaneously, improving overall efficiency and productivity. In addition to enhancing efficiency, chatbots can qualify leads by capturing relevant information from website visitors or prospects. From initial engagement to information gathering and lead nurturing, chatbots can effectively engage and support leads throughout the process.
How Chatbots Have Evolved Over Time
The earliest attempt to develop a chatbot dates back to 1966 with ELIZA, created by Joseph Weizenbaum. ELIZA used pattern matching and substitution techniques to simulate conversation. In the early 2000s, the first AI chatbot named ALICE was developed. This bot operated using a program with an XML schema known as Artificial Intelligence Markup Language (AIML), which helped specify conversation rules and simulate chatting with a real person.
Since the 2000s, advancements in AI and machine learning continued, leading to the launch of personal assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, Cortana, and Amazon Alexa in 2014. Check out our detailed post on the evolution of chatbots and the journey of conversational AI.
In 2021, ChatGPT was introduced by OpenAI. It is a large language model trained on vast amounts of data, generating human-like text based on given input. Following the trend of large language models, Google Gemini (formerly known as Bard) and Microsoft Copilot were also launched. In the future, we can expect significant developments in large language models across various modalities and enhanced accuracy.
How chatbots are deployed in real-world scenarios across industries
Chatbot applications are not limited to any use case or any industry. Chatbots can be deployed for numerous use cases across industries.
69% of consumers were satisfied with their last interaction with a chatbot - Tidio
Here are a few examples of how chatbots are used in real-world scenarios:
Customer Service in E-Commerce:
E-commerce platforms use chatbots to provide instant support for order tracking, product recommendations, and addressing customer inquiries. They enhance the shopping experience by offering real-time assistance.
Healthcare Consultation:
Healthcare chatbots assist users in scheduling appointments, providing basic medical advice, and offering information on medications. They can also help in triage, assessing symptoms, and directing users to appropriate medical resources.
Banking and Finance:
Chatbots in the banking sector handle routine tasks such as balance inquiries, transaction history, and fund transfers. They can also provide information about financial products and assist in resolving common banking issues.
Travel Assistance:
Travel companies deploy chatbots to assist customers with flight bookings, hotel reservations, and travel itineraries. Chatbots can also provide real-time updates on travel conditions and answer frequently asked questions.
Human Resources and Employee Support:
In the workplace, chatbots are used for HR-related tasks, such as answering employee queries about policies, leave requests, and benefits. They can also assist in onboarding processes and training.
Education and Training:
Educational institutions utilize chatbots for student inquiries, course information, and enrolment details. They can also facilitate interactive learning experiences, answer student queries, and provide study resources.
Automotive Sales and Support:
Automotive companies deploy chatbots to assist customers in choosing the right vehicle, scheduling test drives, and providing information on maintenance services. They enhance the overall customer experience in the automotive industry.
Hospitality and Hotel Bookings:
Chatbots are used in the hospitality sector for hotel reservations, check-in/check-out processes, and providing information about amenities. They can also assist guests with room service requests.
Legal Consultation:
Chatbots in the legal industry assist users with basic legal queries, help in generating legal documents, and provide information about legal procedures. They can guide users through initial consultations.
Insurance sector:
Insurance companies deploy chatbots to assist customers in filing claims, checking policy details, and answering questions about coverage. Chatbots can streamline the claims process and provide updates on claim status.
Retail and Customer Engagement:
Retailers use chatbots for personalized product recommendations, order tracking, and handling customer inquiries. They can also assist in loyalty programs and promotional activities.
Government Services:
Governments deploy chatbots to provide information about public services, answer citizen queries, and assist in navigating bureaucratic processes. Chatbots can streamline interactions with government agencies.
Real Estate Sales and Inquiries:
Real estate companies use chatbots to provide property information, schedule property viewings, and answer common questions from potential buyers or tenants.
Food and Restaurant Services:
These examples showcase the versatility of chatbots and their ability to provide value in diverse industries by automating processes, improving customer service, and facilitating more efficient interactions.
Challenges and limitations of Chatbots
Traditional chatbots operate on predefined rules and provide set responses to customer queries. In contrast, Conversational AI chatbots require regular training to address the diverse range of user inquiries and must be monitored for accuracy. If not properly maintained, these chatbots may generate incorrect responses.
GenAI-powered bots are currently considered the most intelligent and accurate. However, they carry an ongoing risk of hallucinations if there is insufficient input data. Additionally, these bots may pose security risks, data leakage, and confidentiality concerns.
Before implementing a GenAI bot, it is essential to consider all these factors. When selecting a chatbot development platform, ensure you evaluate it based on these criteria
Lending and Loan Services :
Chatbots in lending industry streamline processes such as loan applications, eligibility checks and EMI calculations. They assist customers by providing instant updates on loan approval status, repayment schedules & personal financial advice. Chatbots can also automate document collection and verification which reduces processing time and boosts CX.
How to Build a Chatbot for Your Business
If you're planning to deploy a chatbot for your business, the first step is to be clear about the objective. Is it to provide 24x7 support? Reduce customer support costs? Automate lead generation? Whatever the goal, you need to define what your chatbot should be able to do and the kind of queries it should handle.
Here are a few pointers to help you get started:
- Choose the right type of chatbot for your need -Not all chatbots are created equal, and not every type is suitable for your specific use case.
- If you're looking to automate basic, repetitive customer queries, a simple rule-based or AI-powered (intent-based) chatbot will do the job — there's no need to jump straight into LLMs.
- For more complex, dynamic conversations, LLM-based or hybrid bots might be a better fit.
If you’re not sure which one is right for your business, consider using an AI platform like Floatbot.AI to explore the capabilities and then make an informed decision.
-
Choose a No-code/Low-code chatbot platform – Building a chatbot from scratch through code can be time-consuming. Instead, opt for a trusted no-code or low-code chatbot builder, where you can create and launch a bot in minutes.
Look for platforms that offer:
-
Drag-and-drop or prompt-based workflow builders
-
Seamless integrations (CRM, WhatsApp, Email, etc.)
-
Easy AI training and support for LLMs
-
Predefined bot templates to get started quickly
-
- Design the conversational flow
Now comes the fun part — actually deciding how your chatbot will talk. Start with:- Welcome message (Make it warm and helpful)
- What questions will users ask? List them out
- How should the bot respond? Keep it clear and friendly
- Add fallback messages like “Sorry, I didn’t get that.”
- Pro tip: Don’t try to over-automate. Focus on doing a few things really well.
- Train It (If Using AI) - If your bot is AI-powered, you’ll need to give it some data to understand intents and responses. It is very important to include all kind of user intents or possibilities to train AI.
Example:
-
- Intent: “I want to book a demo”
- User examples: “Book a call,” “Schedule a meeting,” “I need a demo”
- The more examples you give, the smarter it becomes.
- Test It Like a Real User - This might seem to be a very obvious step but most of the success of your chatbot depends on this step, it is important to test thoroughly before going live. One bad customer experience with chatbot can lead to bad UX and unsatisfied customer. Hence, before going live, test your bot like you’re the customer. Click every option. Ask weird questions. Try to break it.
Fix anything that feels awkward or confusing. If possible, get a few teammates to test it too. - Go Live and Keep Improving - Once you’re happy with it — launch it on your website, WhatsApp, app, or wherever your customers are.
Then… observe the kind of questions your customers ask
Are users dropping off midway? Are there questions your bot can’t answer? Use that feedback to improve the flow or add more to AI training.
Best Practices for Building a Chatbot
If you are considering deploying a chatbot for your business, the following points will help guide you in building an effective solution.
Check for Integrations and AI Capabilities
Based on your objectives, determine if integration with your backend systems or other platforms is necessary. Identify the number of channels on which the chatbot will be deployed and ensure compatibility with those platforms. Additionally, define the AI capabilities you require; for instance, will the bot use conversational AI or generative AI? Based on the chosen AI approach, create a list of queries and train the bot accordingly. If using generative AI, establish prompts for the bot and define appropriate guardrails.
Consider Security and Compliance
Most bot development platforms offer cloud-based deployments. Depending on your security and compliance needs, choose a platform that provides options for on-premises or cloud deployment. Ensure that the platform adheres to industry standards and understand how user data is handled and utilized.
Scalability and Customization
Scalability is a key consideration. As your business grows, the chatbot should be able to handle a increasing volume of customer interactions without compromising on performance. Additionally, the platform should allow for customization.
Analytics and Reporting
Effective analytics and reporting are important for evaluating the performance of your chatbot. The platform should offer insights into customer interactions, query resolution rates, and usage trends. Real time reporting dashboards will provide the data needed for informed decision making and continuous improvement of your chatbot’s performance.
How to easily build a Gen AI-powered chatbot within a few minutes
A no-code platform lets you build a Conversational AI bot easily without coding. This not only saves chatbot development time but also saves time for integrations with third-party tools or back-end systems. Floatbot comes pre-integrated with multiple platforms and various CCaaS, cPaaS, live chat, digital banking, and insurance platforms.
With Floatbot, you can build workflows, set AI or configure language, live chat, custom look and feel, and more. To set up Gen AI, you simply need to add OpenAI ChatGPT or any other LLM API key, and the bot is ready to handle all the queries through LLM.
Apart from no-code bot building and Gen AI integrations, Floatbot lets you configure an AI execution pipeline for multiple classification models over a user query, Gen AI-powered cognitive search, Agent M – building LLM agents for complex user queries, and Multi-Modal AI for agent assist.
Floatbot is a comprehensive platform that helps you with end-to-end AI automation. Sign up now and give it a try.
Conclusion
Chatbots have become essential tool for modern communication and customer service, which offers businesses a channel to engage with the customers while enhancing operational efficiency. As technology continues to evolve, chatbots have become extremely sophisticated, that can handle complex queries and provide personalized interactions. By understanding the different types of chatbots and their functionalities, businesses can choose the right solution to improve customer experience, streamline processes, and ultimately drive growth. Embracing AI technology is not just a trend; it’s a strategic move towards a more efficient and customer-centric future.